Eurobot Final Host
General InformationAstrakhan
Hosting organization
General Information
 |
Russia is located east of Europe. The most widespread language in the country is Russian. This year's Eurobot Final competition takes place in Astrakhan which is the capital city of the Astrakhan region south-east of Moscow.
Astrakhan is a large administrative, industrial, commercial and cultural center of the Lower Volga region. The city is situated on 11 isles of the Caspian Sea lowland, in the upper part of the Volga Delta and because of this it is surrounded with numerous inland canals.
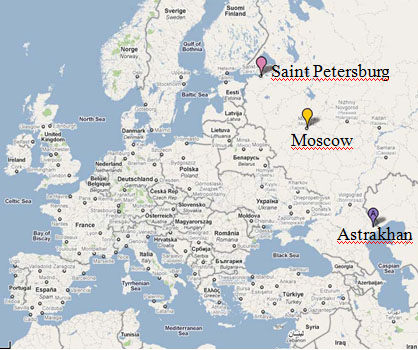 |
An average trip to Astrakhan from around Europe will have transit in Moscow, it will take 2-4 hours in flight to Moscow and another 2 hours in flight to Astrakhan.
Astrakhan belongs to the same time zone as Moscow, although its actual time is 42 minutes ahead of Moscow.
The average monthly temperature in Astrakhan in July is +35C.
The official currency used in Russia is Ruble. Euros and US dollars are common currencies to exchange from in a bank or a special exchange office, however unfavorable exchange rates may apply. ATM services are also available for those with international bank cards.
The city is located on the bank of the Volga river about 50km far from the Caspian sea.
About Astrakhan

Astrakhan is a large administrative, industrial, commercial and cultural center of the Lower Volga region. The city is situated on 11 isles of the Caspian Sea lowland, in the upper part of the Volga Delta and because of this it is surrounded with numerous inland canals.
Astrakhan belongs to the same time zone as Moscow, although its actual time is 42 minutes ahead of Moscow.
The average monthly temperature in Astrakhan in July is +35C.
The river and maritime ports of the Volga and the Caspian Sea basin, international airport and railway stations, which are arranged within the city, will contribute to the organization of convenient transfer for the city guests.
 Astrakhan is justly recognized as the capital of the Caspian states due to the active development of international, commercial and economic relations.
Astrakhan is justly recognized as the capital of the Caspian states due to the active development of international, commercial and economic relations.
There are about 120 large and medium-sized enterprises in the Astrakhan Region, the majority of which is situated in Astrakhan.
Fuel and power industry, represented by JSC "Gazprom Dobycha Astrakhan", developing the Aksaraysk gas condensate field, occupies the leading position. Natural gas and condensate production as well as the extraction of sulfur from hydrogen sulfide is being performed in the steppe, about 60 km away from Astrakhan. "Gazprom Dobycha Astrakhan" is a monopolist in the sulfur production, the largest Russian sulfur exporter in the international market. The industry of the Astrakhan Region is also represented by the wide range of fish-processing and shipbuilding enterprises.
The history of Astrakhan dates back to the 13th century. According to the number of historians the capital of Khazar Kaganat Ityl was located near the modern Astrakhan city in the mid 8th-10th centuries, but the first Astrakhan was mentioned by Arab traveller Ibn Batutta in 1333. At that time it was called Khadzhi-Tarkhan. Khadzhi- Tarkhan was the autumn residence of the Golden Horde khans. The town was considered a large trading center on the way from Persia and India to Russian princedoms and Europe. In 1395 the nomadic hordes of Tamerlan invaded the lands of Golden Horde. Khadzhi-Tarkhan was ravaged and decayed.
In 1556 the Astrakhan Khanate was annexed to Russia by Ivan the Terrible. Our region has been actively developed by the Russians since the 18th century. In 1717 the order of Peter I proclaimed the foundation of the Astrakhan Guberniya.
Nowadays more than 100 nationalities are living in the historically multinational Astrakhan. 14 religious concessions coexist peacefully here, 17 national and cultural associations and 155 non-governmental organizations are carrying out their activities.
There are more than 10 Muslim mosques, a synagogue, Armenian Gregorian Church and Roman Catholic Church in the center of the city. However, the majority of the population of the Astrakhan Region is Orthodox Christians, which is proved by the numerous Orthodox cathedrals and churches located both in the city center and the suburbs.


The central part of the city - historically formed core - represents the isle, washed by the Volga, the Kutum, the Tsarev and the channel Kazachy. On the highest hill there is the white Kremlin of the 16th century. The territory of the Kremlin comprises the Assumption Cathedral - cubic, headed with 5 domes, with a richly decorated frontage and open arched gallery, forming a united architecture complex, including Lobnoe mesto, Trinity Cathedral and many towers. The central part of the city was built up according to the original projects, the embankments with mansions are bounded with the other city parts through numerous bridges. In the center of the former White town (the territory of the Kremlin) the metochions of oriental merchants have remained unchanged. In the 19th century the city was restored, the magnificent mansions, banks, trading houses in the Art Nouveau style were built, which have been the views of the historical center of our city to the present day.


There are 4 theatres in Astrakhan: Astrakhan State Musical Theatre, Astrakhan State Puppet Theatre, Astrakhan State Theatre for Young Spectators and Astrakhan Drama Theatre. The building of the new Musical Theatre - one of the largest and beautiful theatres not only in Astrakhan (Russia), but also in Europe - will be opened soon.

Astrakhan is rich in various museums, exhibition halls and galleries.
Renovated in 2009 the Volga Quay is one of the city places of interest and the most popular place among city residents. In summer the Volga Quay becomes a place for family recreation and provides a wide range of entertainments: from fishing to roller-skating.
 The scientific and educational complex of Astrakhan includes educational institutions of secondary professional and higher education, research institutes and knowledge-intensive enterprises. The number of students of only 3 leading city institutions of higher education (Astrakhan State University, Astrakhan State Technical University and Astrakhan Medical Academy) is more than 35 000 students, what is 14% of the whole young population of 14-30 in the region. The infrastructure of these educational institutions, technical facilities allow to carry out large-scale youth events of international level in Astrakhan.
The scientific and educational complex of Astrakhan includes educational institutions of secondary professional and higher education, research institutes and knowledge-intensive enterprises. The number of students of only 3 leading city institutions of higher education (Astrakhan State University, Astrakhan State Technical University and Astrakhan Medical Academy) is more than 35 000 students, what is 14% of the whole young population of 14-30 in the region. The infrastructure of these educational institutions, technical facilities allow to carry out large-scale youth events of international level in Astrakhan.
In the territory of the Astrakhan region 24 officially registered youth organizations are implementing their activities in the following spheres: patriotic education of youth, development of creative and sportive potential of young people, assistance to intellectual creative work, etc. Volunteer activity is dynamically developing as well.
Hosting organization
Astrakhan State University

The present mission of the ASU is to become an international university complex in the south-east of Russia, forming new scientific, educational and innovative clusters in the regional economy. The functions of the University is both training experts and fundamental researchers and export of educational services as well as transfer of new technologies to industry and business.
The structure of the University comprises 6 institutes:
- Institute of Economics and Law
- Innovative Institute of Natural Science
- Institute of the Humanities
- Innovative Institute of Physics and Mathematics
- Institute of Pedagogics, Psychology and Social Work
- Institute of Language and Professional Communication.
There are 21 schools, 1 college, 83 departments, an affiliated branch in the city of Znamensk.
The University complex consists of 10 educational buildings, 37 computer centers, provided with high speed Internet access and 6 comfortable students' hostels.
The University offers education in more than 100 popular specialties and courses, including 12 programs of professional retraining and 23 programs of advanced training, 16 specialties of professional and technical training.
The graduates of ASU work in governmental, scientific and educational institutions, in the sphere of industry, agriculture and mass media. Nowadays 17 000 students, 600 postgraduate students and PhD-students are studying at the University.
ASU is a member of the Association of the Universities of the Caspian Region. It actively develops international cooperation. In cooperation with partner-universities from Finland, Italy, Croatia, Hungary, Germany, France, China, Iran, Egypt, the USA, Uzbekistan ASU is implementing the following programs: short-term language courses, student exchange, joint scientific and innovative projects, joint student courses and international conferences.
There is the Office of International relations at ASU, which includes Center of Tempus programs (At the present time 6 joint educational programs are being developed together with the partners from France, Belgium, Finland, Great Britain and Germany) and Casa Caspian Nova (Russian and French Center of joint educational programs and research).
In 2007 ASU launched "double degree" Master programs with the University of Nice Sophia Antipolis (France, Nice) and Clark University (USA, Massachusetts).
Students from Iran, Korea, Italy, France, Turkey, Syria, Morocco, Congo and other countries study at the University. Some programs of ASU were evaluated according to ECTS.
ASU has become the first Russian university chosen by Harvard University (USA) for the realization of the educational program on international competitiveness.
ASU aims to create the multilingual educational conditions. Every student or post- graduate student studies 1 or 2 foreign languages during the whole period of education in order to become a competitive specialist and use this knowledge of languages in his or her future professional activity.
ASU is one of the 16 basic Russian institutes which form the University of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. The UNESCO Chair "Learning Society and Social Sustainable Development" operates in the University. Its aim is to form regional system of lifelong education, to settle the issues related to the university joining the Bologna Process, to provide conditions for employment and increasing the level of prosperity of the population, decreasing of social tension, prevention of interethnic and inter- confessional collisions.
ASU is one of the most rapidly developing innovative universities of Eastern Europe that comprises academic traditions and modern technologies.
The speciality "Robots and Robotic Systems" was established on the basis of the Physical and Mathematical Institute of Innovative Development of ASU in 2008. Today this specialty comprises two groups RT-21 and RT-31 of the second and the third study years correspondingly.
The chairs of "Electronics and Technical Physics" and "Information Systems" are the leaders in this speciality. The high-skilled lecturers of these chairs conduct the following courses: "Technology of Robot-Based Manufacturing", "Robots Engines/Drives", "Microprocessor Control of Robots and Their Software", "Robots and Robotic Systems Control", "Artificial Intelligence Methods" etc.
The joint scientific and educational center "Regional Informatization, Control Systems and Mobile Technologies" of ASU and Saint-Petersburg Institute for Computer Science and Automatization of the Russian Academy of Science" (SPICSARAS) carries out its activity on the basis of the University where the students take practical training in the laboratories of control microprocessing equipment and information and measuring systems.
The University also signed partnership contract with chair RK-10 "Robotic Systems" of Moscow State Technical University named after Bauman. 11 young lecturers of ASU are studying at Master School of that chair, what will enable to effect the training of the staff who will hold the special courses at ASU.
ASU actively develops innovative robot workcells and specialized software for their functioning. A large research project "Theoretical Basis and Development of Information Technologies for the Intelligent Systems of Control Automation and Research with Adaptive Mobile Services, Multi-Media Technologies, Technologies of Geoinformation Systems and Methods of Intellectual and Multi-Agent Control of Robotic Workcells" is being implemented on the basis of the scientific and educational centre. The project is financed by federal target programme "Scientific and scientific and pedagogic staff of innovative Russia" (volume of investments is 9 mln. Rub.)
The scientific and educational centre cooperates with small innovative enterprises (SIE) founded by the University. In the cooperation with SIE "Sovremennye Multimediynye Tekhnologii ("Modern Multimedia Technologies")" ltd., "Innorobot" ltd. and "Adaptivnye Mobilnye Servisy" ltd. (Adaptive Mobile Services) a new type of science-intensive product is being developed - an integrated educational and scientific robotic complex. The project is financed by the Foundation for Assistance to Small Innovative Enterprises (volume of investments comprises 12 mln. rub.)
Since 2007 French and Russian Centre for Applied Computer Science and Information Management Systems of the Future Casa Caspian Nova has been conducting its activity at ASU. The area of the centre activity is the implementation of joint Master degree programmes with one of the leading French universities - University of Nice Sofia Antipolis (Nice). In 2007 ASU signed the cooperation agreement with the University of Nice Sofia Antipolis. It was for the first time that Master degree programme "Multi-Media Devices, Data Bases and System Integration" (MBDS) was adopted for teaching in Russia within the framework of this agreement. This one-year French Master degree programme in the sphere of modern information technologies appeared in 1990 under the auspices of industrial partners - IT-companies.Today the programme is focused on the development of multimedia applications with multilevel architecture and wireless technologies.
MBDS deals with the development of prototypes of services ajoint multimedia devices, telecommunication, information transmitting units (chips NFC, RFID, sensing elements), robotic systems.
One of its targets is the integration of innovation technologies NFC into robotic workcells for object identification, navigation indoors and data exchange. The students taking the MBDS Master degree course realized the following prototypes of robotic systems:
1. Robostower - control system for a loader robot in a storehouse on the basis of Bluetooth and NFC-navigation
2. System of robot remote control and semiautonomous charting of a building
3. signalization system on the basis of autonomous mobile robot and conjugate temperature, moisture, illumination and sound detectors.


